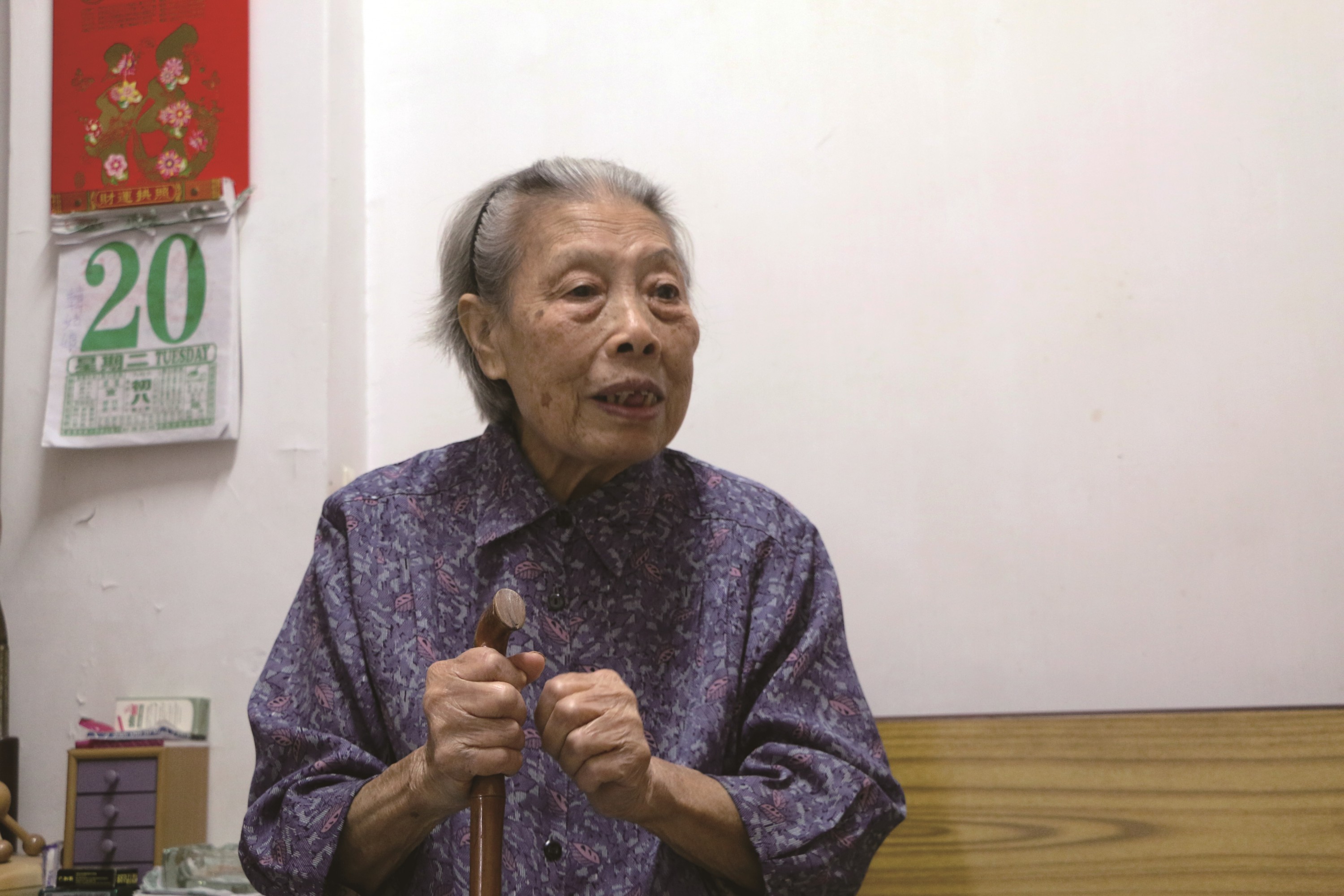
At 92, Cheung Kwan-tue looks back over her life as an amah
By Kelly Wong
The year that Cheung Kuan-tue was born in Guangdong Province, China was ruled by warlords and the Chinese Communist Party held its Third Party Congress in Guangzhou where it discussed forming a possible United Front with the Kuomintang. In her 92 years, Cheung has lived through a brief marriage, war and decades of domestic service as an amah or “mahjeh” in Guangzhou and Hong Kong.

Today, she lives alone in a tidy, self-owned apartment in an old building in Sai Wan Ho. She used to enjoy activities at a local community centre but for the past five or six years, walking has been difficult – it takes an hour to walk the 15 minutes it used to take her to the community centre.
Cheung does not complain of loneliness. Despite limited mobility, she is full of energy and is proud of her independence and self-sufficiency. She is also happy to share the bittersweet story of her life as a mahjeh.
Mahjeh were women employed as live-in servants in wealthy households. The women hailed from the Pearl River Delta Region and most of them had taken vows of celibacy and were known as “self-combed” women. Unlike their married sisters, self-combed women could work outside the home and were economically independent. Some worked in the then flourishing silkworm industry and supported their families. When the industry collapsed in the 1930s many went into domestic service, mainly in Hong Kong, Macau and the Nanyang region (now Singapore and Malaysia).
Cheung was married at an early age but her husband died soon afterwards. Rather than live out her days as a widow, who would have to serve her husband’s family, or remarry, she went to work as an amah when still a teenager. It is a decision she has never regretted. “I came out to work and relied on myself, and I am happy now,” Cheung says.
Cheung’s first job was to work for a rich family in Guangzhou where she was responsible for taking care of children and the elderly. “After the children were sent to school by car, we would wait in the school until they finished,” Cheung recalls with obvious pleasure. “There were so many windows [in the classroom]. I held a pen to learn how to write ‘human’ and ‘big’ in Chinese characters. That is how I know how to write my name.”
The job ended at the tail end of the Chinese Civil War. As Communist forces moved into Guangzhou, Cheung’s wealthy employers had to flee. Therefore, at the age of 26, she moved to Hong Kong alone to continue working as an amah. There she became a member of a community of mahjeh who had turned their back on marriage for various reasons.
Some women took the vow of celibacy because their families were poor and could not afford dowries or needed the fruits of their economic production. Others were themselves resistant to marriage. At a time when feudal traditions strictly governed women’s behaviour and position in society, becoming a self-combing woman was a socially sanctioned way to avoid marriage and be independent.
Self-combing women took a vow of celibacy in a ritual where they would tie their hair and pin it into a bun (sor hei), which is how married women wore their hair. The ceremony was meant to be solemn and it would usually take place in a house where other self-combed women lived. The new member of the sisterhood would take a bath, make food offerings to the gods, and listen to the advice of old self-combed women on the night before the self-combing ceremony.
But by the 1950s, fewer women were willing to take the vow and even those who did might not have taken it very seriously. As Cheung notes: “People could ‘sor hei’ today, and get married tomorrow.”
By Cheung’s time, the rituals were not that strict. “People would just light up the candle and offer incense to the gods. [The self-combed woman’s] hair would be tied into a bun…some actually did not perform the ceremony,” she recalls.